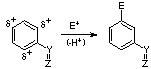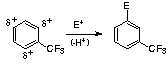Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
Two major effects play a role:
- Resonance Effect
- Inductive Effect:
Resonance Effect:
- Through pi (double bond) system
- Strong effect
- Can be e- Donating (ortho-para directing) or Withdrawing (meta directing)
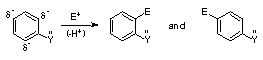
Resonance Donating Effect (ortho-para directing, activates - i.e. more reactive than benzene) - can often be recognized by lone pair of e- on atom directly attached to aromatic ring
Resonance Withdrawing Effect (meta directing, deactivates - i.e. less reactive than benzene) - it can often be recognized by double bond (often with Z=oxygen) conjugated to aromatic ring
Inductive Effect:
- Through sigma (single bond) system
- Weaker effect
- Can be e- Donating (ortho-para directing) or Withdrawing (meta directing)
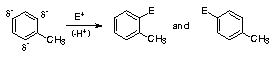
Inductive Donating Effect:(ortho-para directing, activates - i.e. more reactive than benzene) - often caused by an alkyl group
Inductive Withdrawing Effect (meta directing, deactivates - i.e. less reactive than benzene) - often caused haloalkyl group
Multiple Substituents:
- Position of reaction is controlled by strongest donating group
- substitution between meta substituents rare (very difficult because of steric crowding)