We have designed and constructed an astigmatic cell rapid scanning infrared spectrometer to complement the performance of our cavity ring down spectrometer. Although cavity ring down technique offers superior sensitivity for trace absorption, its dynamic range is limited. For molecular systems with sufficient absorption, the rapid scanning technique discussed here is a great choice. The additional advantage of this technique is that a spectrum covering a few wavenumbers can be obtained in a few miliseconds. This makes it a powerful instrument for spectroscopic investigations that require large search ranges.
Ref: Z. Su, W. S. Tam, and Y. Xu, J. Chem. Phys., 2006, 124, 024311.
|
|
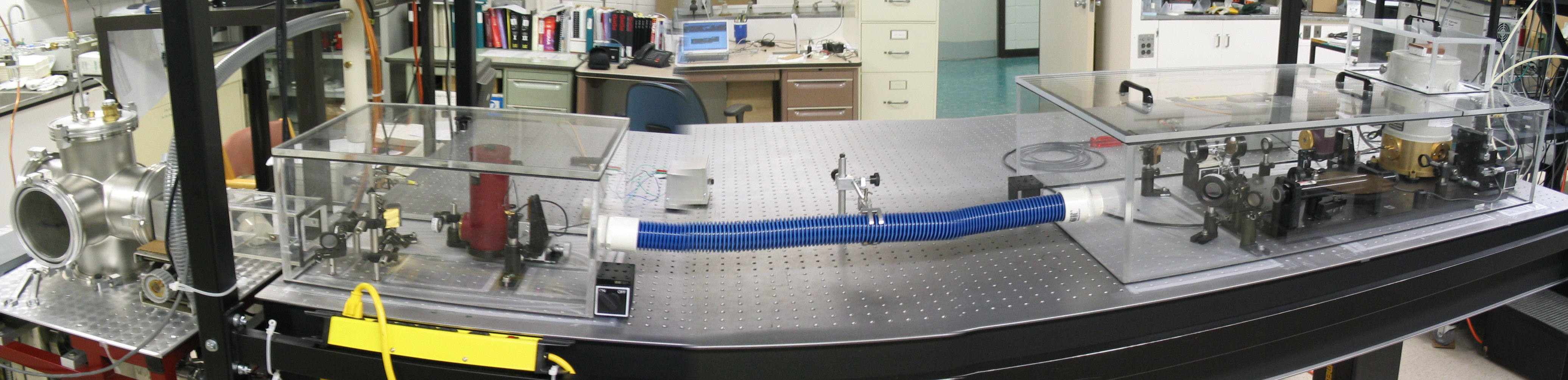
The spectrometer consists of four major components: the vacuum chamber (left) that houses the molecular beam and astigmatic cell assemblies, the infrared detector (middle), the laser source (right), and the hardware and software to control the experiments (not shown).
|
Copyright © 2005 Dr. Xu's lab
|
|

