|
Mid-IR Cavity Ring Down and Cavity Enhanced Spectromters We have designed and constructed several highly specialized spectroscopic instruments such as a cw cavity ring down spectrometer based on lead salt diode lasers and a cavity enhanced absorption spectrometer based on quantum cascade lasers. |
|
|
|
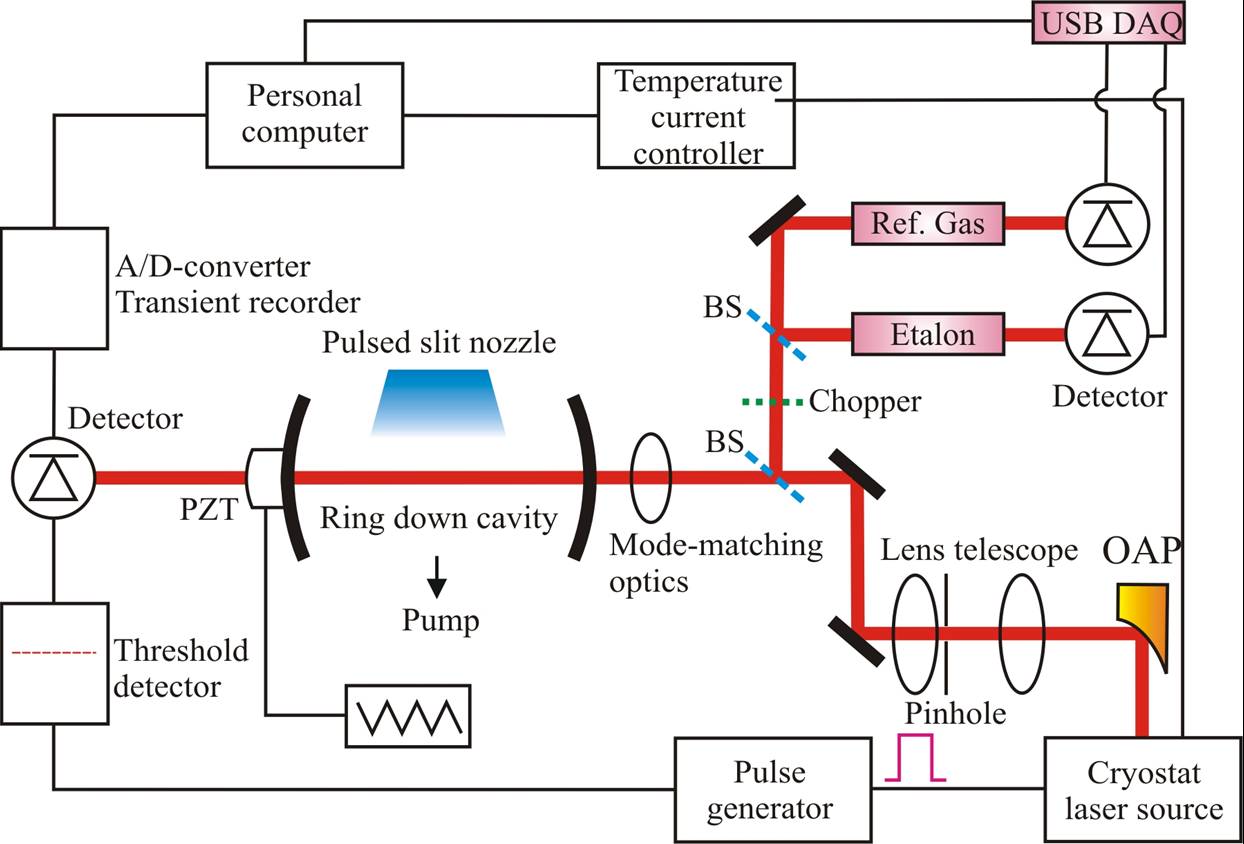
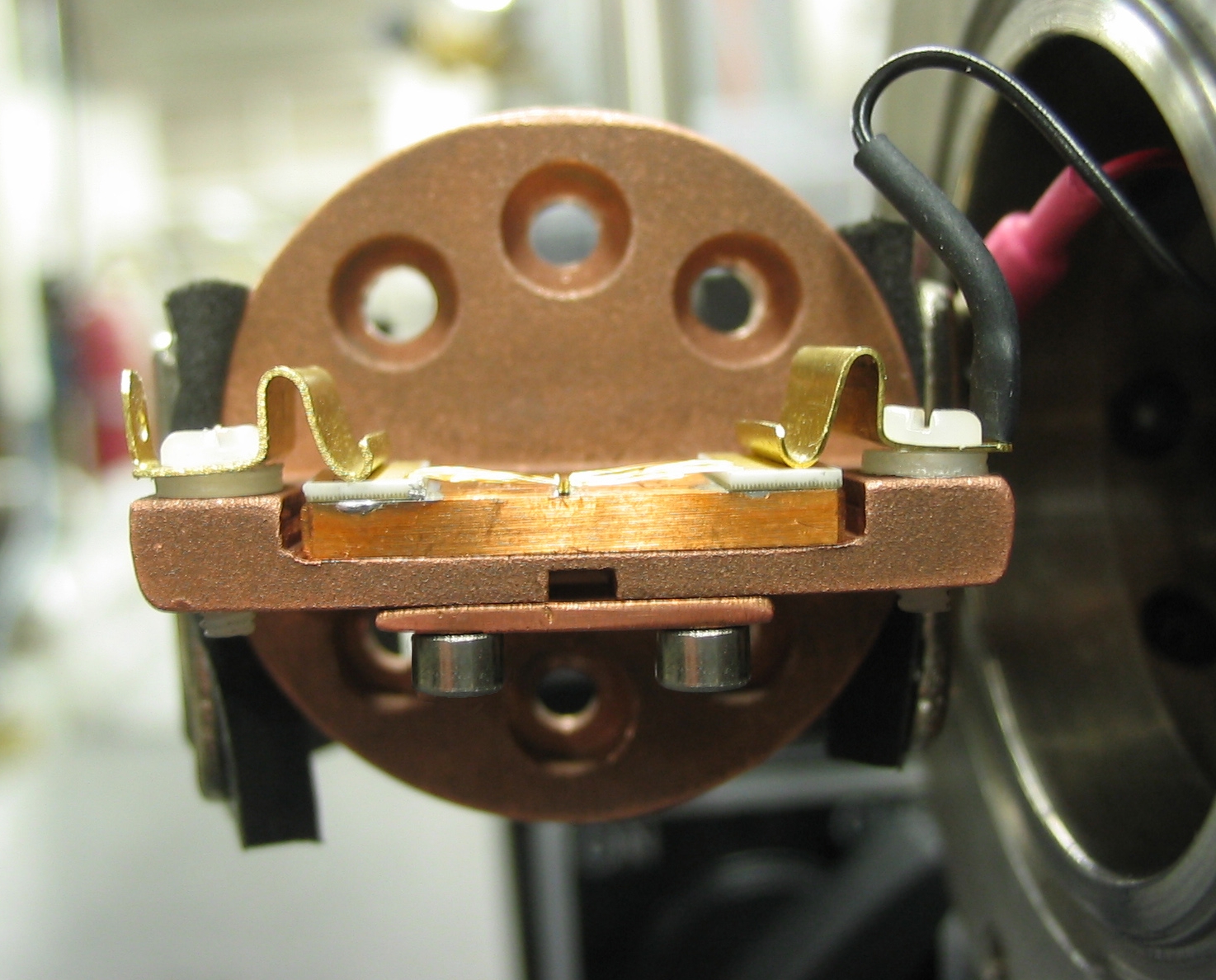
This is one of the key instruments that we designed and constructed. The spectrometer consists of a lead salt diode laser, a very high finess ring down cavity, a slit jet molecular beam assembly, a detection system, and the hardware and software to control the experiments. The central part of the spectrometer (shown on the right) is a six-way vacuum chamber that houses the ring down cavity and the slit jet molecular beam assembly. The chamber is evacuated by a 8000 L/s oil diffusion pump backed by a combination of a roots blower and a rotary pump. This gives us a fast repetition rate of 10 Hz. The diffusion pump is equipped with a liquid nitrogen combination baffle to prevent the back streaming of oil vapour. A LabVIEW computer program was developed to control the experiments.
Ref: W. S. Tam, I. Leonov, and Y .Xu, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 063117.
|
|
|
Quantum cascade lasers are a new generation of powerful miniature lasers based on quantum confinement. In these lasers, electrons cascade down the energy levels created by quantum confinement in ultra-thin alternating layers of semiconducting materials. Unlike conventional semiconductor lasers, whose band gaps are determined by the material, it is possible to produce quantum cascade lasers for any wavelength by changing the design of the layered structure. |
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2003 Dr. Xu's lab
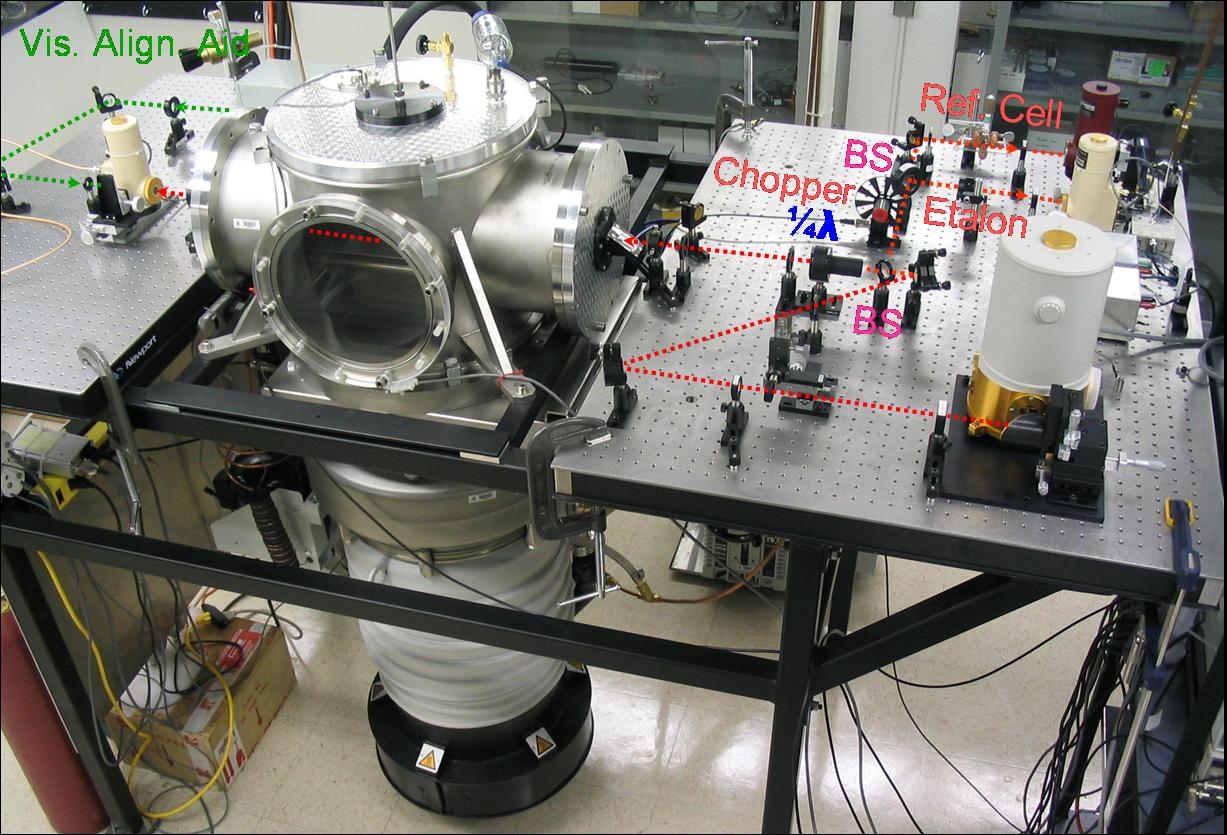
 We have recently set up an infrared spectrometer based on cw quantum cascade laser sources using cavity enhanced absorption and cavity ring down techniques.
We have recently set up an infrared spectrometer based on cw quantum cascade laser sources using cavity enhanced absorption and cavity ring down techniques.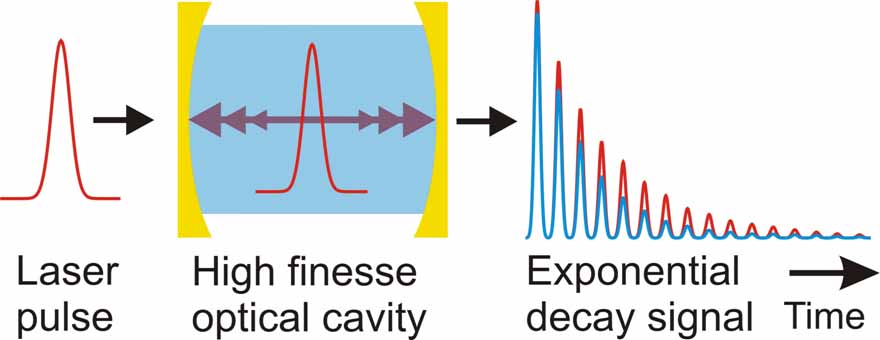 Cavity ring down spectroscopy is a highly sensitive direct absorption technique. It is based on measurement of the rate of absorption rather than the magnitude of absorption of a light pulse. When a short laser pulse is coupled into the cavity that is formed by two highly reflective mirrors, the rate of light coupling out the cavity is a first order exponential decay, exp(-t/τ), where τ is the “ring down” time. The advantages of this technique over the conventional absorption methods are: (i) it is insensitive to the intensity fluctuation of the light source; and (ii) it has an extremely long effective path length (up to several kilometers).
Cavity ring down spectroscopy is a highly sensitive direct absorption technique. It is based on measurement of the rate of absorption rather than the magnitude of absorption of a light pulse. When a short laser pulse is coupled into the cavity that is formed by two highly reflective mirrors, the rate of light coupling out the cavity is a first order exponential decay, exp(-t/τ), where τ is the “ring down” time. The advantages of this technique over the conventional absorption methods are: (i) it is insensitive to the intensity fluctuation of the light source; and (ii) it has an extremely long effective path length (up to several kilometers).