Chem 164/261 - Lecture Outline & Assignment #3
Readings:
Organic Chemistry, L Wade, UA Custom Edition, 2013, Volume 1 (Chem 164/261)
• Functional Group List - Inside Front Cover (also Handout)
• Chapter 6 – Stereochemistry
• Chapter 7 – Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution & Elimination Reactions
Problems:
Do Not turn in, answers available in "Student Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry" for LG Wade
(do all “solved problems” in chapters listed below)
• Chapter 6: 6.1 to 6.8; 6.12; 6.16; 6.19; 6.20; 6.25; 6.26; 6.28; 6.31
• Chapter 7: 7.2; 7.3; 7.7; 7.8a; 7.11; 7.12; 7.14; 7.17; 7.19; 7.20; 7.23; 7.30; 7.34; 7.41; 7.42; 7.43
Lecture Outline 3:
Stereochemistry, Alkyl Halide Substitution (SN1 & SN2) and Elimination (E1 & E2) Reactions
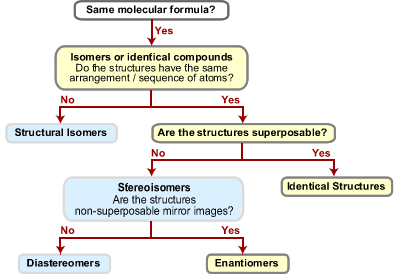
I. Comparison of 2 Structures:
- Chirality and Stereoisomers
- The Concept of Chirality
- Identification of chiral objects and molecules – definitions
- achiral = not chiral
- planes of symmetry within a molecule
- Types of stereoisomers: enantiomers and diastereomers
- Identification of chiral objects and molecules – definitions
- Location of Stereogenic (Chiral) centers – 4 different groups on tetrahedral atom
- Enantiomers and Diastereomers
- Meso compounds - chiral centers with plane of symmetry within molecule
- Molecules with more than one chiral center
- Recognition of chiral centers in complex molecules: cholesterol – 8 chiral centers
- drawing the enantiomer of cholesterol
- relationship of cholesterol and its potential 255 stereoisomers
- Fisher Projections
- R and S Nomenclature
- Rules for assignment of R and S configurations
- Treatment of multiple bonds – example: 3-bromo-1-pentene
- The Concept of Chirality
- Optical Rotation, Optical Purity and Resolution of Enantiomers
- Optical Rotation
- Measurement, factors, and absolute rotation
- Optical purity and enantiomeric excess
- Physical Properties of Enantiomers and Diastereomers
- Racemic mixtures – 50:50 mixtures of enantiomers
- Optical Purity = enantiomeric excess
- Separation (Resolution) of Enantiomers (e.g. Racemic mixtures)
- Creation of diastereomers
- Biological recognition
- Optical Rotation
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions (SN1 and SN2)
- General features of Nucleophilic Substitution vs. Elimination reactions
- Definitions: SN1 and SN2
- Mechanisms
- SN2 Reactions
- Stereochemistry – Walden Inversion (inversion of configuration)
- Substitution of primary and secondary alkyl halides
- Synthesis of alcohols, ethers, other halides, etc.
- Replacement of acetylenic hydrogen
- Acidity of alkynes
- Alkylation – Substitution Reactions
- SN1 Reactions
- Stereochemical aspects (loss of stereochemistry via carbocations)
- Substitution of tertiary alkyl halides and other tertiary carbons
- Synthesis of alcohols, ethers, halides
- General features of Nucleophilic Substitution vs. Elimination reactions
- Elimination Reactions - E1 and E2 Competition with Substitution Reactions (SN1 and SN2)
- El Mechanism – Saytzeff (Zaitsev) Rule, Leaving Groups
- E2 Mechanism – Stereochemistry
- Competition of Elimination Reactions (E2 and E1 vs. SN1 and SN2)