How can organic acids or bases be converted
to a water-soluble form?
1. Organic Acids
Organic acids can be converted to their salt form when treated
with an aqueous solution of inorganic
base (e.g., NaOH (sodium
hydroxide) and NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate)).
Salts
are ionic, and in general, ions are soluble in water
but not soluble in water-immiscible organic solvents.
Remember:
water is a very polar solvent thus salts (i.e.,
ionic species) are well dissolved in it.
1-A. Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are converted to the salt
form with 5% NaOH aqueous solution. NaOH is a strong inorganic base.
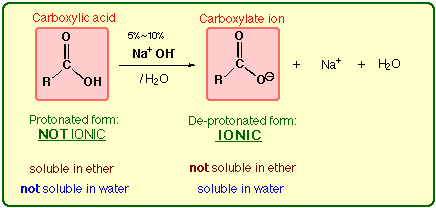
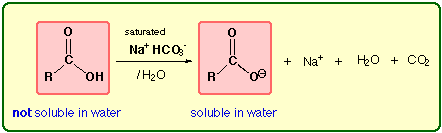
Carboxylic acids are strong organic
acids (pKa = 3 to 4), so they can also be ionized with weak inorganic bases (e.g.,
NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate)) aqueous solution.
Organic Web Chem University of Alberta